XVOF Documentation¶
The time loop is executed in XtentedFiniteVolume.py. Mesh objects are responsible of the cells and nodes objects. So in principle, the entry point calls a mesh method which calls a cell or node method to update variables. The following documentation specifies the role of all functions and modules in the code.
Cell¶
Package for cell modules
-
class
cell.Cell(nbr_of_cells: int)¶ A Cell object represents all the mesh cells. Its different members are, for most of them, numpy 1D-array of nbr_of_cells length.
Memory layout is the same as in C/C++, i-e ‘row wise’.
-
abstract
compute_mass()¶ Compute mass of the cells
-
abstract
compute_new_density(mask)¶ Compute the new density in the cells
- Parameters
- mask (np.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify cells to be computed
-
abstract
compute_new_porosity(time_step, porosity_model, mask)¶ Compute the new porosity according to the porosity model in XDATA :param time_step: float :param porosity_model: porosity model to compute :type mask: np.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool)
-
abstract
compute_new_pressure(mask, delta_t)¶ Compute the pressure in the cells at time t + dt
-
abstract
compute_new_pseudo(time_step, mask)¶ Compute the new value of artificial viscosity in the cells
- Parameters
- time_step (float) – time step
- mask (np.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify cells to be computed
-
abstract
compute_new_size(*args, **kwargs)¶ Compute the new size of the cells
-
abstract
compute_new_time_step(mask)¶ Compute the new value of critical time step in the cells
- Parameters
- mask (np.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify cells to be computed
-
abstract
compute_size(topology, node_coord)¶ Compute the size of the cells
- Parameters
- topology (Topology) – topology of the mesh
- node_coord (numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – array of nodal coordinates
-
property
density¶ Density in the cells
-
property
dt¶ Critical time step in cells
-
property
energy¶ Internal energy in the cells
-
property
fields_manager¶ Return a copy of the field manager
-
classmethod
get_coordinates(nbr_cells, topology, x_coord, y_coord=None, z_coord=None)¶ Return the vector of cell center coordinates at time t
- Parameters
- nbr_cells – number of cells
- topology (Topology) – topology
- x_coord (numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – x coordinate vector
- y_coord (numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – y coordinate vector
- z_coord (numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – z coordinate vector
- Returns
the vector of cell center coordinates at time t
- Return type
numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, topology.dimension], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
increment_variables()¶ Variables incrementation
-
initialize_cell_fields(mask_node_target, mask_node_projectile, topology)¶ Initialisation of the cell fields and attributes of cell_in_target and cell_in_projectile
- Parameters
- mask_node_target (numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool, order='C')) – bool array for nodes in the target
- mask_node_projectile (numpy.array([nbr_of_cells, 1], dtype=bool, order='C')) – bool array for nodes in the target
- topology (Topology) – mesh connectivity object
-
property
mass¶ Mass of the cells
-
property
number_of_cells¶ Number of cells
-
property
porosity¶ Porosity
-
property
pressure¶ Pressure in the cells
-
print_infos()¶ Print the fields in the cells
-
property
pseudo¶ Artificial viscosity in the cells
-
property
shear_modulus¶ Elastic shear modulus
-
property
size_t¶ Size (length, area, volume) of the cells at time t
-
property
size_t_plus_dt¶ Size (length, area, volume) of the cells at time t + dt
-
property
sound_velocity¶ Sound velocity in the cells
-
property
stress¶ Cauchy stress tensor in the cells
-
property
stress_xx¶ Cauchy stress tensor in the cells. 1D : component xx
-
property
stress_yy¶ Stress tensor field : sigma_yy
-
property
stress_zz¶ Stress tensor field : sigma_zz
-
property
yield_stress¶ Yield stress separating elastic from plastic behavior
-
abstract
-
class
cell.OneDimensionCell(number_of_elements: int)¶ A class for one dimension cells
-
classmethod
add_elastic_energy_method(dt, density_current, density_new, stress_dev_current, stress_dev_new, strain_rate_dev)¶ Take into account the additional term in internal energy due to elasticity
- Parameters
- dt – time step
- density_current – density at time t
- density_new – density at time t+dt
- stress_dev_current – stress deviator at time t
- stress_dev_new – stress deviator at time t+dt
- strain_rate_dev – deviator of the strain rate tensor at time t+dt/2
-
classmethod
apply_equation_of_state(cell: xfv.src.cell.cell.Cell, eos, density: numpy.array, density_new: numpy.array, pressure: numpy.array, pressure_new: numpy.array, energy: numpy.array, energy_new: numpy.array, pseudo: numpy.array, cson_new: numpy.array)¶ Apply the equation of state to get the new internal energy, pressure and sound speed
- Parameters
- cell – cell collection [in]
- eos – equation of state object [in]
- density – array of current density [in]
- density_new – array of new velocity [in]
- pressure – array of current pressure [in]
- pressure_new – array of new pressure [out]
- energy – array of current energy [in]
- energy_new – array of new energy [out]
- pseudo – array of artificial viscosity [in]
- cson_new – array of sound speed [out]
-
apply_plasticity(mask, delta_t)¶ Apply plasticity treatment if criterion is activated : - compute yield stress - tests plasticity criterion - compute plastic strain rate for plastic cells
- Parameters
- mask – boolean array to identify cells to be computed
- dt – time step
-
property
artificial_viscosity_field¶ Pseudoviscosity field
-
property
classical¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which cells are classical
-
compute_complete_stress_tensor()¶ Compute the Cauchy stress tensor (sum of pressure, artificial viscosity and deviatoric stress)
-
static
compute_deviator_strain_rate(dt, topology, node_coord_new, node_velocity_new)¶ Compute strain rate deviator
- Parameters
- mask – mask to select classical cells
- dt – time step
- topology – table of connectivity : link between cells and nodes id
- node_coord_new – array with new nodes coordinates
- node_velocity_new – array with new nodes velocities
-
compute_deviatoric_stress_tensor(mask, topology, node_coord_new, node_velocity_new, delta_t)¶ Compute the deviatoric part of the stress tensor
- Parameters
- mask – mask to select classical cells
- topology – table of connectivity : link between cells and nodes id
- node_coord_new – array with new nodes coordinates (time n+1)
- node_velocity_new – array with new nodes velocities (time n+1/2)
- delta_t – time step (staggered tn+1/2)
-
compute_mass()¶ Compute mass of the cells
-
compute_new_density(mask)¶ Computation of the density of the cells at time t+dt using mass conservation principle
- Parameters
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – array of boolean to identify classical cells
-
compute_new_porosity(delta_t: float, porosity_model, mask)¶ Compute the new porosity according to the porosity model in XDATA
- Parameters
- delta_t – model to compute the shear modulus
- porosity_model – porosity model to compute
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – mask to identify the cells to be computed
-
compute_new_pressure(mask, dt)¶ Computation of the set (internal energy, pressure, sound velocity) for v-e formulation
-
compute_new_pseudo(delta_t: float, mask)¶ Computation of cells artificial viscosity at time t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify classical cells
-
compute_new_size(topology, node_coord, mask)¶ Computation of the cells length at time t+dt
- Parameters
- topology (Topology1D) – table to link nodes and cells index
- node_coord (np.array([nbr_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64)) – array with the nodes coordinates at time t+dt
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify classical cells
-
compute_new_time_step(mask)¶ Computation of the time step in the cells at time t+dt
- Parameters
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – boolean array to identify classical cells
-
classmethod
compute_pseudo(delta_t: float, rho_old: numpy.array, rho_new: numpy.array, size_new: numpy.array, cel_son: numpy.array, a_pseudo: float, b_pseudo: float)¶ Computation of artificial viscosity
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
- rho_old – density at time t
- rho_new – density at time t+dt
- size_new – cell size at time t+dt
- cel_son – sound speed at time t
- a_pseudo – quadratic pseudo coefficient
- b_pseudo – linear pseudo coefficient
-
compute_shear_modulus(shear_modulus_model, mask)¶ Compute the shear modulus G according to the constitutive elasticity model in XDATA
- Parameters
- shear_modulus_model – model to compute the shear modulus
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – mask to identify the cells to be computed
-
compute_size(topology, node_coord)¶ Computation of the cells initial length
- Parameters
- topology (Topology1D) – table to link nodes and cells index
- node_coord (np.array([nbr_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64)) – array with nodes coordinates
-
classmethod
compute_time_step(cfl, cfl_pseudo, rho_old, rho_new, size_new, sound_speed_new, pseudo_old, pseudo_new)¶ Computation of the time step
- Parameters
- cfl – nombre cfl
- cfl_pseudo – cfl linked to the shock treatment stability condition
- rho_old – density at time t
- rho_new – density at time t+dt
- size_new – size of element
- sound_speed_new – sound velocity at time t+dt
- pseudo_old – artificial viscosity at time t
- pseudo_new – artificial viscosity at timet+dt
-
compute_yield_stress(yield_stress_model, mask)¶ Compute the yield stress according to plasticity constitutive model in XDATA
- Parameters
- yield_stress_model – model to compute the yield stress
- mask (np.array([nbr_cells, 1], dtype=bool)) – mask to identify the cells to be computed
-
property
density_field¶ Density field
-
property
deviatoric_stress_current¶ Return the current deviatoric stress tensor Sxx Syy Szz
-
property
deviatoric_stress_new¶ Return the new deviatoric stress tensor Sxx Syy Szz
-
property
energy_field¶ Internal energy field
-
property
enriched¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which cells are enriched
-
property
equivalent_plastic_strain_rate¶ Return the equivalent plastic strain rate
-
static
general_method_deviator_strain_rate(dt, x_new, u_new)¶ Compute the deviator of strain rate tensor (defined at the center of the cell) from the coordinates and velocities interpolated at the center of the cell
- Parameters
- dt – time step (float)
- x_new – coordinates array at time n+1 of the left and right nodes of each cell.
- u_new – velocity array at time n+1/2 of the left and right nodes of each cell
Note
x_new, u_new shape is (size(mask), 2)
- x_new is an array : array([coord_node_left, coord_node_right] * nbr_cells in the mask)
- u_new is an array : array([velocity_node_left, velocity_node_right] * nbr_cells in the mask)
-
impose_pressure(ind_cell: int, pressure: float)¶ Pressure imposition
- Parameters
- ind_cell – index of the cells
- pressure – pressure value to be imposed
-
increment_variables()¶ Increment cells variables from one iteration to another
-
property
plastic_strain_rate¶ Return the current plastic stain rate tensor Dp_xx Dp_yy Dp_zz
-
property
porosity_field¶ Porosity field
-
property
pressure_field¶ Pressure field
-
classmethod
-
class
cell.OneDimensionHansboEnrichedCell(n_cells: int)¶ A collection of 1d enriched elements. Treatment for Hansbo enrichment
-
apply_plasticity_enr(mask_mesh, delta_t)¶ Apply plasticity treatment if criterion is activated :
- compute yield stress
- tests plasticity criterion
- compute plastic strain rate for plastic cells
-
property
artificial_viscosity_field¶ - Returns
- artificial viscosity field
- Return type
- np.array
-
cell_enr_increment()¶ Increment the enriched cell variables
-
property
classical¶ - Returns
- a mask where True indicate a classical cell
-
classmethod
compute_discontinuity_borders_velocity(disc, node_velocity)¶ Compute the velocities of points at the discontinuity border
- Parameters
- disc – Discontinuity to be considered
- node_velocity – array with nodes velocity
- Return ug
velocity of the discontinuity left boundary
- Return ud
velocity of the discontinuity right boundary
-
compute_enriched_deviatoric_strain_rate(dt: float, node_coord_new: numpy.array, node_velocity_new: numpy.array) → None¶ Compute the deviatoric strain rate for enriched cells
- Parameters
- dt – time step
- node_coord_new – array, new nodes coordinates
- node_velocity_new – array, new nodes velocity
-
compute_enriched_deviatoric_stress_tensor(node_coord_new, node_velocity_new, delta_t)¶ Compute the deviatoric part of the stress tensor
- Parameters
- node_coord_new – array, new nodes coordinates
- node_velocity_new – array, new nodes velocity
- delta_t – float, time step
-
compute_enriched_elements_new_density()¶ Compute the new densities for left and right parts of the ruptured element (from mass conservation equation)
-
compute_enriched_elements_new_part_size(time_step, node_velocity)¶ Compute the new size of each ruptured element part (left size and right size)
- Parameters
- time_step – time step
- node_velocity – array, node velocities
-
compute_enriched_elements_new_pressure(delta_t)¶ Compute pressure, internal energy and sound velocity in left and right parts of the enriched elements
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
compute_enriched_elements_new_pseudo(delta_t)¶ Compute the new artificial viscosity of the enriched_cells
- Parameters
- delta_t – time_step
-
compute_enriched_elements_new_time_step()¶ Compute the new local time step. The calculation is equivalent to a remeshing time step and thus underestimates the time step for the enriched cells
-
compute_enriched_shear_modulus(shear_modulus_model)¶ Compute the shear modulus for ruptured cell
- Parameters
- shear_modulus_model – model to compute the shear modulus
-
compute_enriched_stress_tensor()¶ Compute the complete enriched stress tensor : sigma = -(p+q) I + S
-
compute_enriched_yield_stress(yield_stress_model)¶ Compute the yield stress for ruptured cells
- Parameters
- yield_stress_model – model to compute the yield stress
-
property
density_field¶ - Returns
- density field
- Return type
- np.array
-
property
deviatoric_stress_field¶ - Returns
- (deviateur de sigma)_xx field
- Return type
- np.array
-
property
energy_field¶ - Returns
- energy field
- Return type
- np.array
-
property
enr_artificial_viscosity¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell artificial viscosity field
-
property
enr_density¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell density field
-
property
enr_deviatoric_strain_rate¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell deviatoric strain rate at time t
-
property
enr_deviatoric_stress_current¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell deviatoric stress at time t
-
property
enr_deviatoric_stress_new¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell deviatoric stress at time t+dt
-
property
enr_energy¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell internal energy field
-
property
enr_equivalent_plastic_strain_rate¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell equivalent plastic strain rate at time t
-
property
enr_plastic_strain_rate¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell plastic strain rate tensor at time t
-
property
enr_pressure¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell pressure field
-
property
enr_shear_modulus¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell shear modulus field
-
property
enr_sound_velocity¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell sound speed field
-
property
enr_stress¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell stress at time t
-
property
enr_stress_xx¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell stress at time t
-
property
enr_yield_stress¶ Accessor on the right part of cracked cell yield stress field
-
property
enriched¶ - Returns
- a mask where True indicates an enrich cell
-
initialize_additional_cell_dof(disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity)¶ Values to initialize the right part fields when discontinuity disc is created
- Parameters
- disc – the current discontinuity
-
property
left_part_size¶ Accessor on the size of the left part of cracked cell field
-
property
pressure_field¶ - Returns
- pressure field
- Return type
- np.array
-
print_infos()¶ - Printing informations about Elements
- A REECRIRE AU PROPRE; NOTATIONS ONT CHANGE
-
reconstruct_enriched_elasto_field(classical_field: numpy.array, enriched_field_name: str)¶ True field reconstruction from the classical and enriched fields
- Parameters
- classical_field – classical field
- enriched_field_name – name of the enriched field
- Returns
complete field
- Return type
np.array
-
reconstruct_enriched_hydro_field(classical_field: xfv.src.fields.field.Field, enriched_field_name: str)¶ True field reconstruction from the classical and enriched fields
- Parameters
- classical_field – classical field
- enriched_field_name – name of the enriched field
- Returns
complete field
- Return type
np.array
-
property
right_part_size¶ Accessor on the size of the right part of cracked cell field
-
property
stress_xx_field¶ - Returns
- sigma_xx field
- Return type
- np.array
-
-
cell.consecutive(data: numpy.ndarray, stepsize=1)¶ Return an array in which each item is an array of contiguous values of the original data array
- Parameters
- data – the array to be splitted in continuous arrays
- stepsize – the difference between tow values that are considered contiguous
Cohesive Zone Model¶
Package for cohesive zone model modules
-
class
cohesive_model.CohesiveLaw(cohesive_law_points: numpy.array)¶ A class for cohesive law implementation
-
compute_cohesive_force(opening)¶ Returns the cohesive force associated with the given opening
- Parameters
- opening – discontinuity opening
- Returns
- float
-
classmethod
interpolate_cohesive_law(opening, separation_1, separation_2, stress_1, stress_2)¶ Interpolate the value of cohesive stress between points 1 and 2
- Parameters
- opening – discontinuity opening
- separation_1 – separation at point 1
- separation_2 – separation at point 2
- stress_1 – stress at point 1
- stress_2 – stress at point 2
- Returns
cohesive stress
-
-
class
cohesive_model.CohesiveZoneModel(cohesive_law_points: numpy.array, unloading_model: xfv.src.cohesive_model_unloading.unloading_model_base.UnloadingModelBase)¶ A class for the computation of the cohesive force
-
compute_cohesive_stress(disc)¶ Compute the cohesive force for the current opening of discontinuity according to the current discontinuity opening
- Parameters
- disc – discontinuity
-
Cohesive Zone Model : unloading options¶
Package for unloading the cohesive zone model modules
-
class
cohesive_model_unloading.UnloadingModelBase(*args, **kwargs)¶ A model for unloading reloading path in cohesive zone model
-
abstract
compute_unloading_reloading_condition(disc, new_opening)¶ Compute the cohesive stress in case of unloading or reloading condition (new_opening is less than the discontinuity maximal opening
- Parameters
- disc – discontinuity
- new_opening – opening of the discontinuity
- Returns
cohesive stress (float)
-
abstract
-
class
cohesive_model_unloading.ConstantStiffnessUnloading(slope)¶ A model for unloading reloading path with constant stiffness
-
compute_unloading_reloading_condition(disc, new_opening)¶ Compute the cohesive stress in case of unloading or reloading condition (new_opening is less than the discontinuity maximal opening
- Parameters
- disc – discontinuity
- new_opening – opening of the discontinuity
- Returns
cohesive stress (float)
-
-
class
cohesive_model_unloading.LossOfStiffnessUnloading¶ A model for unloading reloading path with decreasing stiffness
-
compute_unloading_reloading_condition(disc, new_opening)¶ Compute the cohesive stress in case of unloading or reloading condition (new_opening is less than the discontinuity maximal opening
- Parameters
- disc – discontinuity
- new_opening – opening of the discontinuity
- Returns
cohesive stress (float)
-
Contact¶
Package for contact modules
-
class
contact.ContactBase(*args, **kwargs)¶ An interface for all cohesive zone model
-
abstract
compute_contact_force(node_velocity: numpy.array, disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity, delta_t: float) → float¶ Checks if contact and apply correction
- Parameters
- node_velocity – node velocity array
- disc – discontinuity to examine
- delta_t – time step
-
abstract
-
class
contact.LagrangianMultiplierContact¶ A class for contact management using Lagrangian multipliers
-
compute_contact_force(node_velocity: numpy.array, disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity, delta_t: float) → float¶ Checks if contact and apply correction
- Parameters
- node_velocity – node velocity array
- disc – discontinuity to examine
- delta_t – time step
-
-
class
contact.PenaltyContact(penalty_stiffness)¶ A class to manage contacts using penalty method
-
compute_contact_force(node_velocity: numpy.array, disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity, delta_t: float) → float¶ Checks if contact and apply correction
- Parameters
- node_velocity – node velocity array
- disc – discontinuity to examine
- delta_t – time step
-
Customized Boundary Condition Functions¶
Package for customized boundary condition shape functions modules
-
class
custom_functions.CustomFunction¶ A generic CustomFunction class that should be used to derive more specific custom function class
-
abstract
evaluate(time, *args, **kwargs)¶ Returns the value of the function evaluated at time
- Parameters
- time – the required time
- args – other arguments
- kwargs – other keywords arguments
- Returns
the value
-
is_pressure()¶ Return true if the instance is a pressure
-
is_velocity()¶ Return true if the instance is a velocity
-
register_pressure()¶ Register the current instance as a pressure
-
register_velocity()¶ Register the current instance as a velocity
-
abstract
-
class
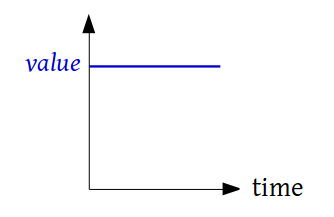
custom_functions.ConstantValue(value)¶ This class defines a function that returns a constant value
-
evaluate(time, *args, **kwargs)¶ Returns the value of the function evaluated at time
- Parameters
- time – the required time
- Returns
- the value
-
-
class
custom_functions.MarchTable(data_file)¶ This class defines a value interpolated from a text file
-
evaluate(time, *args, **kwargs)¶ Return the value of the for the time given in argument
- Parameters
- time – current time
- Returns
- the value
-
-
class
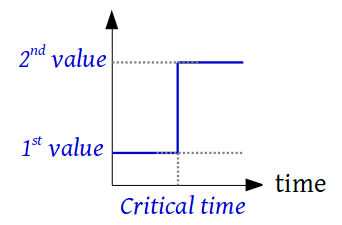
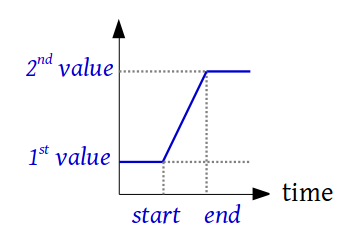
custom_functions.Ramp(first_value, second_value, start_time, end_time)¶ A class that defines a ramp between 2 constants steps
-
property
end_time¶ Return the time at which the slope ends
-
evaluate(time, *args, **kwargs)¶ Returns the value of the function evaluated at time
- Parameters
- time – the required time
- Returns
- the value
-
property
first_value¶ Return the first value
-
property
second_value¶ Return the second value
-
property
start_time¶ Return the time at which the slope begins
-
property
Data¶
Package for reading the case data modules
-
class
data.DataContainer(datafile_path: Union[str, pathlib.Path])¶ This class provides access to all the data found in the json datafile
Discontinuity¶
Package for discontinuity modules
-
class
discontinuity.Discontinuity(cell_id: int, mask_in_nodes: numpy.array, mask_out_nodes: numpy.array, discontinuity_position_in_ruptured_element: float, enriched_mass_matrix_props: xfv.src.data.enriched_mass_matrix_props.EnrichedMassMatrixProps)¶ A class describing a discontinuity 1D
-
compute_discontinuity_new_opening(node_position: numpy.array)¶ Compute the discontinuity opening
- Parameters
- node_position – coordinates of the nodes
-
classmethod
discontinuity_list()¶ Returns the list of all existing discontinuities
-
classmethod
discontinuity_number()¶ Returns the number of existing discontinuities
-
enr_increment()¶ Increment the variables of discontinuity
-
classmethod
get_discontinuity_associated_with_cell(cell_id: int)¶ Loop on the discontinuities collection to find the one that contain the cell cell_id
- Parameters
- cell_id – cell id to find
- Returns
- Discontinuity or None if no disc is found
-
property
get_ruptured_cell_id¶ Returns the id of ruptured cell for the discontinuity
-
has_mass_matrix_been_computed()¶ Set the __mass_matrix_updated boolean to True
-
property
label¶ Accessor on label variable
- Returns
- label
-
property
mask_disc_nodes¶ Accessor on the mask on the nodes of the discontinuity
- Returns
- the mask on the nodes “concerned” by the discontinuity
-
property
mask_in_nodes¶ Accessor on the mask on the nodes “in” the discontinuity
- Returns
- the mask on the nodes “in” the discontinuity
-
property
mask_out_nodes¶ Accessor on the mask on the nodes “out” the discontinuity
- Returns
- the mask on the nodes “out” the discontinuity
-
property
mass_matrix_updated¶ Accessor on the boolean that indicates if the mass matrix has been computed
- Returns
- the boolean that indicates if the mass matrix has been computed
-
property
position_in_ruptured_element¶ Accessor on the relative position of the discontinuity in ruptured element
-
reinitialize_kinematics_after_contact()¶ Set the new velocity to the old one to cancel the increment that has lead to contact
-
Equation Of State¶
Package for equation of state modules
-
class
equationsofstate.EquationOfStateBase¶ An interface for all equation of states
-
abstract
solve_volume_energy(specific_volume, internal_energy, pressure, derivative, vson=None)¶ Solve the eos with [v, e] formulation
-
abstract
-
class
equationsofstate.MieGruneisen(czero=3940.0, S1=1.489, S2=0.0, S3=0.0, rhozero=8930.0, grunzero=2.02, b=0.47, ezero=0.0)¶ Mie Gruneisen equation of state
-
property
eos_param¶ Accessor on equation of state parameters :return:
-
solve_volume_energy(specific_volume, internal_energy, pressure, derivative, vson=None)¶ Given the specific volume and internal energy computes the pressure, sound speed and derivative of the pressure with respect to the internal energy
- Parameters
- specific_volume (numpy.array) – specific volume (in)
- internal_energy (numpy.array) – internal energy (in)
- pressure (numpy.array) – pressure (out)
- derivative (numpy.array) – derivative of pressure with respect to the internal energy (out)
- vson (numpy.array) – sound speed (out)
-
property
Fields¶
Package for field management modules
-
class
fields.Field(size, current_value=0.0, new_value=0.0)¶ Classical physical field on cells or nodes. Owning current and future values in numpy.arrays
-
property
current_value¶ - Returns
- the current field value
- Return type
- numpy.array
-
increment_values()¶ Increment field values
-
property
new_value¶ - Returns
- the future field value
- Return type
- numpy.array
-
property
size¶ - Returns
- the size of the field (i.e number of cells or nodes on which the field is defined)
-
property
FigureManager (animation)¶
Package for figure management modules
-
class
figure_manager.PhysicFigure(X, Y, xlabel='X', ylabel='Y', titre='titre', interface_id=0, save_path=None)¶ Figure
-
set_x_limit(val_min=0.0, val_max=1.0)¶ Fixation des limites en x
-
set_y_limit(val_min=0.0, val_max=1.0)¶ Fixation des limites en y
-
update(abscissa=None, ordinate=None, title_comp=None)¶ Update image to get animation And save the image if a path is given
-
-
class
figure_manager.FigureManager(mesh_instance, dump=False)¶ A manager for figures and animations during calculation
-
create_figure_for_cell_field(field_x, field_y)¶ Creation of figures for cell fields. Abscissa is thus the cell coordinates
- Parameters
- field_x – abscissa of the figure
- field_y – ordinate of the figure
-
create_figure_for_node_field(field_x, field_y)¶ Creation of figures for nodal fields. Abscissa is thus the node coordinates
- Parameters
- field_x – abscissa of the figure
- field_y – ordinate of the figure
-
create_reps()¶ Creation of the reps where data is saved
-
populate_figs()¶ Creation of the figures associtated with fields and add to the list of figures
-
set_iteration_controler(deltat_it: float)¶ The figures will be updated every delta_it iterations
- Parameters
- deltat_it – interval between two figures
-
set_time_controler(deltat_t: float)¶ The figures will be updated every delta_t seconds
- Parameters
- deltat_t – interval between two figures
-
update(time, iteration)¶ If the current time given in argument is above the time of next output then the manager asks each of its database to save fields. It’s the same for a current iteration above the iteration of next output
- Parameters
- time – simulation time
- iteration – id of the current iteration
-
update_fields()¶ Update the fields to plot using the mesh update methods
-
update_figs(title_compl=None)¶ Update the fields and the associated figures
- Parameters
- title_compl – title of the figure
-
Mass Matrix¶
Package for mass matrix modules
-
class
mass_matrix.EnrichedMassMatrix(size_of_mass_matrix)¶ A class to factorize code for the enriched mass matrix
-
abstract
assemble_enriched_mass_matrix(*sub_matrix_names)¶ Assemble and inverse the mass matrix after enrichment
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix(discontinuity, topology, cells_mass)¶ Compute the enriched mass matrix for Hansbo shape functions (associated with 1 discontinuity)
- Parameters
- discontinuity – discontinuity to be considered
- topology – topology = connectivity
- cells_mass – array of cells mass
-
abstract
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_left_part(mass_0: float, mass_1: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the left part DDL are organized : 0 : N1g and 1 : N2g
- Parameters
- mass_0 – mass of the element right on the left of the cracked cell
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
abstract
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_right_part(mass_1: float, mass_2: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the right part DDL are organized : 2 : N2d and 3: N1d
- Parameters
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- mass_2 – mass of the element right on the right of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
abstract
get_mass_matrix_left()¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the left part of the cracked cell
-
abstract
get_mass_matrix_right()¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the right part of the cracked cell
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_classic_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for classical degrees of freedom
- Returns
- the extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for classical dof
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_enriched_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched degrees of freedom
- Returns
- extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched dof
-
abstract
print_enriched_mass_matrix()¶ Print the mass matrix * (with aligned members)
-
abstract
rearrange_dof_in_inv_mass_matrix()¶ Rearrange dof to easily compute the node velocity with classical and enriched dof separately
-
abstract
-
class
mass_matrix.EnrichedMassMatrixConsistent¶ A class for the consistent enriched mass matrix
-
assemble_enriched_mass_matrix(*sub_matrix_names)¶ Assemble and inverse the mass matrix after enrichment
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_left_part(mass_0: float, mass_1: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the left part DDL are organized : 0 : N1g and 1 : N2g
- Parameters
- mass_0 – mass of the element right on the left of the cracked cell
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_right_part(mass_1: float, mass_2: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the right part DDL are organized : 2 : N2d and 3: N1d
- Parameters
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- mass_2 – mass of the element right on the right of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
get_mass_matrix_left()¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the left part of the cracked cell
-
get_mass_matrix_right()¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the right part of the cracked cell
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_classic_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for classical degrees of freedom
- Returns
- the extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for classical dof
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_coupling_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for coupling between classical and enriched degrees of freedom
- Returns
- the coupling part of the inverse of the mass matrix
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_enriched_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched degrees of freedom
- Returns
- extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched dof
-
print_enriched_mass_matrix()¶ Print the mass matrix * (with aligned members)
-
rearrange_dof_in_inv_mass_matrix()¶ Rearrange dof to easily compute the node velocity with classical and enriched dof separately
-
-
class
mass_matrix.EnrichedMassMatrixLump¶ A class for the lumped enriched mass matrix
-
assemble_enriched_mass_matrix(*sub_matrix_names)¶ Assemble and inverse the mass matrix after enrichment
-
abstract
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_left_part(mass_0: float, mass_1: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the left part DDL are organized : 0 : N1g and 1 : N2g
- Parameters
- mass_0 – mass of the element right on the left of the cracked cell
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
abstract
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_right_part(mass_1: float, mass_2: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the right part DDL are organized : 2 : N2d and 3: N1d
- Parameters
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- mass_2 – mass of the element right on the right of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
get_mass_matrix_left() → numpy.array¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the left part of the cracked cell
-
get_mass_matrix_right() → numpy.array¶ Accessor on the part of mass matrix concerning the right part of the cracked cell
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_classic_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for classical degrees of freedom
- Returns
- the extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for classical dof
-
property
inverse_enriched_mass_matrix_enriched_dof¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched degrees of freedom
- Returns
- extraction of the inverse of the mass matrix for enriched dof
-
print_enriched_mass_matrix()¶ Print the mass matrix * (with aligned members)
-
rearrange_dof_in_inv_mass_matrix()¶ Rearrange dof to easily compute the node velocity with classical and enriched dof separately
-
-
class
mass_matrix.EnrichedMassMatrixLumpMenouillard¶ A class for the lumped enriched mass matrix for Menouillard lumping
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_left_part(mass_0: float, mass_1: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the left part DDL are organized : 0 : N1g and 1 : N2g
- Parameters
- mass_0 – mass of the element right on the left of the cracked cell
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_right_part(mass_1: float, mass_2: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the right part DDL are organized : 2 : N2d and 3: N1d
- Parameters
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- mass_2 – mass of the element right on the right of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
-
class
mass_matrix.EnrichedMassMatrixLumpSum¶ A class for the enriched mass matrix lumped with sum of lines of the consistent enriched mass matrix
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_left_part(mass_0: float, mass_1: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the left part DDL are organized : 0 : N1g and 1 : N2g
- Parameters
- mass_0 – mass of the element right on the left of the cracked cell
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
compute_enriched_mass_matrix_right_part(mass_1: float, mass_2: float, epsilon: float)¶ Compute the Hansbo mass matrix for the right part DDL are organized : 2 : N2d and 3: N1d
- Parameters
- mass_1 – mass of the cracked cell
- mass_2 – mass of the element right on the right of the cracked cell
- epsilon – relative position of the disc inside the cracked cell
-
-
class
mass_matrix.OneDimensionMassMatrix(number_of_nodes, consistent_matrix_on_last_cells=False)¶ A class for 1d mass matrix
-
compute_correction_mass_matrix_for_cell_500(cell_mass_vector, mask_node, topologie)¶ Compute the exact form of mass matrix (classical) , no lumping
- Parameters
- cell_mass_vector – vector of cells mass
- mask_node – id of cell to be considered
- topologie – topology
-
compute_mass_matrix(topology, cell_mass_vector, node_number_by_cell_vector)¶ Compute the mass matrix and its inverse according to Wilkins method
- Parameters
- topology – topology of the simulation
- cell_mass_vector – cells mass vector
- node_number_by_cell_vector – number of nodes per cell (vector)
-
property
inverse_correction_mass_matrix¶ Accessor on the inverse of the exact mass matrix
- Returns
- the inverse of the exact mass matrix
-
property
inverse_mass_matrix¶ Accessor on the inverse of the mass matrix
- Returns
- the inverse of the mass matrix
-
property
mass_matrix¶ Accessor on _mass_matrix
-
property
mass_matrix_correction¶ Accessor on _mass_matrix
-
-
class
mass_matrix.SymNDArray¶ Une classe pour les matrices symétriques
-
mass_matrix.compute_wilkins_mass_matrix(topology, cell_mass_vector, node_number_by_cell_vector)¶ Compute nodal mass by averaging the mass of neighbouring cells (Wilkins method)
- Parameters
- topology (Topology) – topology of the simulation
- cell_mass_vector (numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – cells mass vector
- node_number_by_cell_vector (numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, 1], dtype=np.int64, order='C')) – number of nodes per cell (vector)
-
mass_matrix.multiplication_masse(matrix, vector)¶ Fonction pour faire le produit matriciel matrice * vecteur adapté pour la matrice masse sous forme de vecteur
:param matrix : matrix (array multiD) :param vector: vector (array 1D)
>>> import numpy as np >>> matrice = np.array([1., 2., 3., 4.]) >>> vecteur = np.array([1., 1./2., 1./3., 1./4.]) >>> multiplication_masse(matrice, vecteur) array([ 1., 1., 1., 1.]) >>> matrice_bis = np.array([[1., 2., 3., 4.], [2., 4., 0.5, -1], [3., 0.5, 1., -2.], [4., -1, -2., 3.]]) >>> vecteur_bis = np.array([1., 1./2., 1./4., 1./4.]) >>> multiplication_masse(matrice_bis, vecteur_bis) array([ 3.75 , 3.875, 3. , 3.75 ])
-
mass_matrix.inverse_masse(matrix)¶ MassMatrix de type MassMatrix Fonction pour faire inverse la matrice masse, qu’elle soit sous forme de vecteur ou de matrice
- Parameters
- matrix – matrix to inverse
-
mass_matrix.lump_matrix(matrix)¶ Condense la matrice de masse avec la méthode de Menouillard (on somme sur toute la ligne pour obtenir une matrice diagonale)
- Parameters
- matrix – matrix to lump
Mesh¶
Package for mesh modules
-
class
mesh.Mesh1dEnriched(initial_coordinates, initial_velocities)¶ This class defines a one dimensional mesh with potential enrichment
-
apply_contact_correction(delta_t: float)¶ Compute the contact force to be applied to ensure non penetration of the discontinuities boundaries
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
apply_elasticity(delta_t, shear_modulus_model, mask_material)¶ Compute the deviatoric part of stress tensor
- Parameters
- delta_t – float, time step staggered
- shear_modulus_model – model to compute the shear modulus
- mask_material – array of bool to select cells of interest
-
apply_plasticity(delta_t: float, yield_stress_model, plasticity_criterion, mask_mesh: numpy.array)¶ Apply plasticity treatment if criterion is activated :
- compute yield stress
- tests plasticity criterion
- compute plastic strain rate for plastic cells
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
- yield_stress_model – model to compute the yield stress
- plasticity_criterion – model for the plasticity criterion
- mask_mesh – mask cells in projectile or target
-
apply_pressure(surface, pressure)¶ Apply a given pressure on left or right boundary
- Parameters
- surface (str ('left' | 'right')) – name of the surface where pressure has to be imposed
- pressure (float) – value of the pressure to impose
-
apply_rupture_treatment(treatment, time: float)¶ Apply the rupture treatment on the cells enforcing the rupture criterion
- Parameters
- treatment (RuptureTreatment) – rupture treatment
- time – simulation time
-
apply_velocity_boundary_condition(surface, velocity)¶ Apply a given velocity on left or right boundary
-
property
artificial_viscosity_field¶ Artificial viscosity field
-
assemble_complete_stress_tensor()¶ Assembling pressure and stress deviator
-
property
cells_coordinates¶ Cells coordinates (coordinates of cells centers)
-
compute_cells_masses()¶ Cell mass computation
-
compute_cells_sizes()¶ Computation of cells sizes at t
-
compute_new_cells_densities()¶ Computation of cells densities at t+dt
-
compute_new_cells_porosity(delta_t: float, porosity_model)¶ Computation of porosity model for each cell at t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
- porosity_model – model to compute the porosity model
-
compute_new_cells_pressures(delta_t: float)¶ Computation of cells pressure at t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
compute_new_cells_pseudo_viscosity(delta_t: float)¶ Computation of cells artificial viscosity at t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
compute_new_cells_sizes(delta_t)¶ Computation of cells sizes at t+dt
-
compute_new_cohesive_forces()¶ Computation of cohesive forces at t+dt
-
compute_new_nodes_coordinates(delta_t: float)¶ Computation of nodes coordinates at t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
compute_new_nodes_forces()¶ Computation of nodes forces at t+dt
-
compute_new_nodes_velocities(delta_t: float)¶ Computation of nodes velocities at t+dt
- Parameters
- delta_t – time step
-
compute_new_time_step()¶ Computation of new time step
-
compute_nodes_masses()¶ Nodal mass computation
-
property
density_field¶ Density field
-
property
deviatoric_stress_field¶ Deviatoric stress field
-
property
energy_field¶ Internal energy field
-
static
get_discontinuity_list()¶ Returns the list of existing discontinuities
-
get_ruptured_cells(rupture_criterion)¶ Find the cells where the rupture criterion is checked and store them
- Parameters
- rupture_criterion (RuptureCriterion) – rupture criterion
-
increment()¶ Moving to next time step
-
property
nodes_coordinates¶ Nodes coordinates
-
property
porosity_field¶ Porosity field
-
property
pressure_field¶ Pressure field
-
property
shear_modulus_field¶ Shear Modulus
-
property
stress_xx_field¶ First component of the Cauchy stress tensor
-
property
topology¶ Returns the topology object (in order to get it accessible for unittests)
-
property
velocity_field¶ Node velocity field
-
property
yield_stress_field¶ Yield Stress
-
-
class
mesh.Topology(nbr_of_nodes, nbr_of_cells, dim=1)¶ A class to manage mesh topology and objects connectivity
-
add_cell_in_contact_with_node(ind_node: int, ind_cell: int)¶ Register a cell ind_cell as belonging to the node ind_node
- Parameters
- ind_cell – cell index connected to ind_node
- ind_node – node index connected to ind_cell
-
property
cells_in_contact_with_node¶ Returns the array for cells <-> nodes connectivity
-
property
dimension¶ Return the dimension of the mesh
-
get_cells_in_contact_with_node(ind_node: int)¶ Returns the cell indexes connected to the node ind_node
- Parameters
- ind_node – node index
-
get_nodes_belonging_to_cell(ind_cell: int)¶ Returns the node indexes connected to the cell ind_cell :param ind_cell: cell_index
-
property
nodes_belonging_to_cell¶ Returns the array for nodes <-> cells connectivity
-
set_nodes_belonging_to_cell(ind_cell, ind_node_list)¶ Register a node list as belonging to the cell ‘ind_cell’
- Parameters
- ind_cell (int) – cell index
- ind_node_list (list) – list of the node index connected to ind_cell
-
-
class
mesh.Topology1D(nbr_of_nodes, nbr_of_cells)¶ 1D specialization of the Topology class
>>> my_topo = Topology1D(11, 10) >>> my_topo.get_cells_in_contact_with_node(0) array([ -1, 0]) >>> my_topo.get_cells_in_contact_with_node(5) array([4, 5]) >>> my_topo.get_nodes_belonging_to_cell(9) array([ 9, 10]) >>> my_topo.get_cells_in_contact_with_node(np.array([1, 3])) array([[0, 1], [2, 3]]) >>> my_topo.cells_in_contact_with_node[:] array([[ -1, 0], [ 0, 1], [ 1, 2], [ 2, 3], [ 3, 4], [ 4, 5], [ 5, 6], [ 6, 7], [ 7, 8], [ 8, 9], [ 9, -1]])
-
add_cell_in_contact_with_node(ind_node, ind_cell)¶ Register a cell ind_cell as belonging to the node ind_node
- Parameters
- ind_cell – cell index connected to ind_node
- ind_node – node index connected to ind_cell
-
Nodes¶
Package for nodes module
-
class
node.Node(nbr_of_nodes, position_initiale, dim=1, vitesse_initiale=None)¶ Un objet Node représente l’ensemble des noeuds du maillages. Ses différents membres sont essentiellement des vecteurs de nbr_of_nodes lignes. Plusieurs colonnes peuvent être présentes selon la dimension du problème à traiter.
L’organisation en mémoire est comme en C/C++ c’est à dire ‘row wise’. C’est pour cette raison que les lignes de chacun des vecteurs représentent les noeuds. Ce faisant on a par exemple tous les X des noeuds contigus en mêmoire. (vectorisation, localisation spatiale)
-
compute_new_coodinates(mask: numpy.array, delta_t: float)¶ Calcul de la coordonnée au temps t+dt
- Parameters
- mask – mask to select some specific nodes
- delta_t – time step
-
abstract
compute_new_force(*args, **kwargs)¶ Compute the nodal forces
-
abstract
compute_new_velocity(delta_t, mask, matrice_masse)¶ Compute the velocity at time t+dt/2
- Parameters
- delta_t – staggered timestep
- mask – boolean array to identify nodes to be computes
-
property
dimension¶ Dimension du problème
- Returns
- dimension du problème
- Return type
- int
-
property
enriched¶ Returns an array of the status of all nodes False = classical node True = enriched node
- Returns
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes], dtype=bool)
-
property
force¶ Forces nodales
- Returns
- vecteur des forces nodales
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
increment()¶ Update the node velocities and coordinates
-
infos(index)¶ Affichage des informations concernant le noeud d’indice index
- Parameters
- index (int) – indice du noeud à afficher
-
property
masse¶ Masses nodales
- Returns
- vecteur des masses nodales
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, 1], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
property
number_of_nodes¶ Nombre de noeuds du problème
- Returns
- dimension du problème
- Return type
- int
-
property
umundemi¶ Vitesses au demi pas de temps précédent
- Returns
- vitesses des noeuds au demi pas de temps précédent
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, dim], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
property
upundemi¶ Vitesses au demi pas de temps suivant
- Returns
- vitesses des noeuds au demi pas de temps suivant
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, dim], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
property
xt¶ Positions des noeuds au temps t
- Returns
- positions des noeuds au temps t
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, dim], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
property
xtpdt¶ Positions des noeuds au temps t + dt
- Returns
- positions des noeuds au temps t + dt
- Return type
- numpy.array([nbr_of_nodes, dim], dtype=np.float64, order=’C’)
-
-
class
node.OneDimensionNode(nbr_of_nodes, poz_init, vit_init, section=1.0)¶ A class to manage all the nodes in a 1d mesh
-
apply_correction_reference_bar(delta_t, inv_complete_mass_matrix, inv_wilkins_mass_matrix, mask)¶ Apply a correction on velocity field to compute velocity from exact(non lumped) mass matrix for elements in mask
-
apply_pressure(ind_node, pressure)¶ Apply pressure on a given node
- Parameters
- ind_node (int) – node index to apply the pressure at
- pressure (float) – pressure to be applied
-
apply_velocity_boundary_coundition(ind_node, velocity)¶ Appliquer une CL en vitesse sur le noeud ind_node
- Parameters
- ind_node –
- velocity –
- Returns
-
property
classical¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which nodes are classical
-
compute_complete_velocity_field()¶ Compute the true field of nodal velocity
-
compute_new_force(topologie, contrainte, classical_cell_mask: numpy.array)¶ Calcul des forces agissant sur les noeuds
- Parameters
- topologie (Topology) – topologie du calcul
- contrainte (numpy.array([nbr_of_node-1, 1], dtype=np.float64, order='C')) – tenseur des contriante de cauchy sigma xx
- classical_cell_mask – masks of the classical cells
-
compute_new_velocity(delta_t, mask, matrice_masse)¶ Computes the node velocities at time t+dt/2
- Parameters
- delta_t (float) – pas de temps
- mask (boolean array) – boolean array to select non enriched nodes
- matrice_masse – inverse de la matrice de masse
-
property
enrichment_not_concerned¶ By definition, a node is concerned by enrichment if one of his connected cell is enriched, ie if its evolution is modified by enrichment :return: boolean mask indicating which nodes are concerned by enrichment
-
infos(index)¶ Affichage des informations concernant le noeud d’indice index
- Parameters
- index (int) – node index to print
-
property
section¶ Surface associated with a node
-
property
velocity_field¶ True field of the node velocities
-
-
class
node.OneDimensionHansboEnrichedNode(nbr_of_nodes: int, initial_positions: numpy.array, initial_velocities: numpy.array, section=1.0)¶ A class for the enriched nodes with Hansbo enrichment
-
apply_force_on_discontinuity_boundaries_arr(force: numpy.ndarray) → None¶ Transport the force to apply on discontinuity boundaries on the classical and enriched nodes
- Parameters
- force – value of the force to apply
-
property
classical¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which nodes are classical
-
compute_complete_velocity_field()¶ Compute the true field of node velocity
-
compute_enr_new_velocity(disc, delta_t)¶ Compute the new velocity enriched degree of freedom
- Parameters
- disc – the current discontinuity
- delta_t – float, time step
-
compute_enriched_nodes_cohesive_forces(cohesive_model)¶ Compute the cohesive forces for the enriched nodes
- Parameters
- cohesive_model – cohesive model
-
compute_enriched_nodes_new_force(contrainte_xx: numpy.array, enr_contrainte_xx)¶ Compute the enriched force on enriched nodes and apply correction for classical force on enriched nodes (classical ddl)
- Parameters
- contrainte_xx – vecteur contrainte xx, array de taille (nb_cell, 1)
- enr_contrainte_xx – vecteur contrainte xx enrichie, array de taille (nb_cell, 1)
-
coupled_enrichment_terms_compute_new_velocity(disc, delta_t)¶ Compute the coupled terms between classical and enriched dof due to non diagonal complete mass matrix. Takes into account nodes concerned by enrichment and not only the enriched nodes
- Parameters
- disc – the current discontinuity
- delta_t – time step
-
property
enriched¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which nodes are enriched
-
static
enriched_nodes_compute_new_coordinates(disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity, delta_t: float)¶ Compute the new nodes coordinates after enrichment
- Parameters
- disc – current discontinuity
- delta_t – time step
-
property
enrichment_concerned¶ By definition, the nodes concerned by enrichment have non null enriched shape function on their support
- Returns
- boolean mask indicating which nodes are concerned by enrichment
-
property
enrichment_not_concerned¶ - Returns
- boolean mask indicating which nodes are not concerned by enrichment
-
infos(index)¶ Print information
-
initialize_additional_node_dof(disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity)¶ Initialialise les ddl enrichis aux noeuds
- Parameters
- disc – Discontinuity
-
reinitialize_kinematics_after_contact(disc: xfv.src.discontinuity.discontinuity.Discontinuity)¶ Set the new velocity to the old one to cancel the increment that has lead to contact
- Parameters
- disc – discontinuity to be considered
-
property
velocity_field¶ Accessor on the true node velocity field
-
Outputs¶
Package for output management modules
-
class
output_manager.OutputDatabase(path_to_hdf5)¶ A class to store simulation fields in an hdf5 database
-
add_field(f_name, values, **kwargs)¶ Create a dataset corresponding to field_name and storing the values. All extra keywords arguments are stored as attributes of the dataset
- Parameters
- f_name – name of the field to be added
-
add_time(time)¶ Create an hdf5 group containing all fields for the current time
- Parameters
- time – time to be added
-
close()¶ Close the database
-
-
class
output_manager.OutputManager¶ The manager of all outputs
-
finalize()¶ Close all the database
-
get_value_of_field(field: xfv.src.output_manager.outputmanager.Field, owner) → numpy.array¶ Get the np.array associated to the field following all the attribute names list
- Parameters
- field – field to be extracted
- owner – object who supports the fields
-
register_all_fields(enrichment_registration, cells, nodes, database_id)¶ Add all fields to the manager.
- Parameters
- enrichment_registration – bool to control if the enriched fields should be registered
- cells – cells from which fields must be printed
- nodes – nodes from which fields must be printed
- database_id – identifier of the database
-
register_database_iteration_ctrl(database_name, database_obj, delta_it)¶ Add a database to the manager. The database will be updated every delta_it iterations
-
register_database_time_ctrl(database_name, database_obj, delta_t)¶ Add a database to the manager. The database will be updated every deltat_t seconds
-
register_field(field_name, field_support, field_attr_name, indexes=None, database_names=None)¶ Add a field to the manager. Each field will be stored in every database in arguments if specified else in every database registered
-
update(time, iteration, eps, discontinuity_list)¶ If the current time given in argument is above the time of next output then the manager asks each of its database to save fields. It’s the same for a current iteration above the iteration of next output
Additional_dof_fields are created when a new discontinuity is created. Need to treat them in a different way from classical fields. Based on this remark, enr_fields have standard name “Additional…” Differentiation is made with test startswith(Additional)
-
-
class
output_manager.OutputTimeControler(identifier, time_period=None, iteration_period=None)¶ Compute the time or iteration of outputs
-
db_has_to_be_updated(time: float, iteration: int) → bool¶ Return True if the iteration or time requires to write fields in the database and update the next output time or iteration.
- Parameters
- time – current time
- iteration – current iteration
-
-
class
output_manager.OutputDatabaseExploit(path_to_db)¶ A class for exploiting the output stored in Hdf5 database
-
extract_discontinuity_opening(time)¶ Read database to extract the discontinuity opening, cohesive force and a bool to filter results
- Parameters
- time – time which to extract data at
-
extract_field_at_time(field_name, time)¶ Return the value of the specified field at time time in a numpy array
- Parameters
- field_name – name of the field to be extracted
- time – time at which the field has to be extracted
- Returns
the values of the field at time time
-
extract_fields_for_cohesive_zone_model(cracked_cell_index, time)¶ Read database to extract the discontinuity opening, cohesive force and a bool to filter results
- Parameters
- cracked_cell_index – cell id containing the cohesive zone
- time – time which to extract data at
-
extract_true_field_at_time(field_type, time)¶ Return the value of the true field at time time in a numpy array
- Parameters
- field_type – type of the true field (“Pressure”, “Density” …)
- time – time at which the field has to be extracted
- Returns
the values of the true field at time time
-
get_cells_coordinate(time)¶ Return the cells center coordinate at time time
- Parameters
- time – time at which the cells coordinates are computed
- Returns
- the cells center coordinates
-
get_cells_true_size_at_time(time)¶ Return the cells true sizes at time time
- Parameters
- time – time at which the cells sizes are computed
- Returns
- the cells true sizes
-
get_nodes_coordinates(time)¶ Extract nodes coordinates from database
-
property
nb_saved_times¶ Return the number of time step that have been saved
- Returns
- the number of time step that have been saved
-
property
saved_fields¶ Return the different fields stored in the database
- Returns
- the different fields stored in the database
-
property
saved_fields_type¶ Return the different fields type stored in the database
- Returns
- the different fields type stored in the database
-
property
saved_times¶ Return the list of saved times
- Returns
- the list of saved times
-
-
output_manager.build_node_true_field(classical_field, enrichment_type=None)¶ Build the node true field based on the node status
- Parameters
- classical_field – field of classical values
- enriched_field – field of enriched values
- node_status – boolean mask where True indicates an enriched item
- enrichment_type – type of enrichment
- Returns
the node true field
-
output_manager.build_cell_true_field(classical_field, enriched_field, enrichment_type)¶ Build the cell true field based on the cell status
- Parameters
- classical_field – field of classical values
- enriched_field – field of enriched values
- enrichment_type – type of enrichment. Moes ou Hansbo (utile pour reconstruction)
- Returns
the cell true field
>>> import numpy as np >>> a = np.array([1., 2., 1.]) >>> b = np.array([0., 0.5, 0.]) >>> s = np.array([False, True, False]) >>> build_cell_true_field(a, b, s).tolist() [1.0, 1.5, 2.5, 1.0] >>> b = np.array([0.25, 0., 0.]) >>> s = np.array([True, False, False]) >>> build_cell_true_field(a, b, s).tolist() [0.75, 1.25, 2.0, 1.0] >>> a = np.array([1., -2., 2., 3., -7, 10.]) >>> b = np.array([0., -2., 0., 0., 2., 0.]) >>> s = np.array([False, True, False, False, True, False]) >>> build_cell_true_field(a, b, s).tolist() [1.0, 0.0, -4.0, 2.0, 3.0, -9.0, -5.0, 10.0] >>> a = np.array([-3., 2., 1., -3., -5, 9.]) >>> b = np.array([0., -2., 3., 0., 0., 0.]) >>> s = np.array([False, True, True, False, False, False]) >>> build_cell_true_field(a, b, s).tolist() [-3.0, 4.0, 0.0, -2.0, 4.0, -3.0, -5.0, 9.0]
Plasticity criterion¶
Package for plasticity criterion modules
-
class
plasticitycriterion.PlasticityCriterion¶ An abstract base class for plasticity criteria
-
abstract static
check_criterion(cells)¶ Check the plasticity criterion on the cells in arguments
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
-
abstract static
check_criterion_on_right_part_cells(cells)¶ Check the plasticity criterion on the discontinuity in arguments
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
-
abstract static
-
class
plasticitycriterion.VonMisesCriterion¶ A plasticity criterion based on Von Mises model
-
check_criterion(cells)¶ Return the mask of the cells where the VonMises plasticity criterion is verified
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
- Returns
- the mask of the cells where the VonMises plasticity criterion is verified
-
static
check_criterion_on_right_part_cells(cells)¶ Return the mask of the cells where the VonMises plasticity criterion is verified
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
- Returns
- the mask of the cells where the VonMises plasticity criterion is verified
-
Rheology¶
Package for rheology modules
-
class
rheology.ShearModulus(initial_value)¶ Abstract class for the shear modulus computation
-
abstract
compute(density: numpy.array) → numpy.array¶ Compute the new value of shear modulus
- Parameters
- density – the current density
- Returns
- the computed shear modulus
-
abstract
-
class
rheology.ConstantShearModulus(init_value)¶ Class for constant shear modulus
-
compute(density: numpy.array) → numpy.array¶ Compute the shear modulus => returns constant value of shear modulus
- Parameters
- density – the current density
- Returns
- the computed shear modulus
-
Rupture criterion¶
Package for rupture criterion modules
-
class
rupturecriterion.RuptureCriterion¶ An abstract base class for rupture criteria
-
abstract
check_criterion(cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Check of the rupture criterion on the cells in arguments :param cells: cells on which to check the criterion
-
abstract
-
class
rupturecriterion.HalfRodComparisonCriterion(ruptured_cell_index=500)¶ A not physical rupture criterion to validate XFEM by comparing results to other results obtained without XFEM on a half rod
-
check_criterion(cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Return the mask of the cells where only the ruptured_cell_index is set to True
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check criterion
- Returns
- mask of the cells where only the ruptured_cell_index is set to True
-
-
class
rupturecriterion.DamageCriterion(d_limite)¶ A rupture criterion based on damage value
-
check_criterion(cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Return the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
- Returns
- the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure
-
-
class
rupturecriterion.MinimumPressureCriterion(pmin)¶ A rupture criterion based on minimal pressure
-
check_criterion(cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Return the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure :param cells: cells on which to check the criterion :return: the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure
-
-
class
rupturecriterion.MaximalStressCriterion(sigma_max)¶ A rupture criterion based on minimal pressure
-
check_criterion(cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Return the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure
- Parameters
- cells – cells on which to check the criterion
- Returns
- the mask of the cells where pressure is below the minimum pressure
-
Rupture treatments¶
Package for failure treatment modules
-
class
rupturetreatment.RuptureTreatment¶ An interface for rupture treatments
-
abstract
apply_treatment(cells, ruptured_cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Application of the treatment on the ruptured cells
- Parameters
- cells – array of all cells
- ruptured_cells – boolean array marking the ruptured cells
-
abstract
-
class
rupturetreatment.ImposedPressure(pressure)¶ A treatment of rupture by imposing pressure
-
apply_treatment(cells, ruptured_cells, *args, **kwargs)¶ Apply the rupture treatment by imposing the pressure on the ruptured cells
- Parameters
- cells – array of all cells
- ruptured_cells – boolean array marking the ruptured cells
-
-
class
rupturetreatment.EnrichElement(position_rupture: float, lump_matrix: xfv.src.data.enriched_mass_matrix_props.EnrichedMassMatrixProps)¶ A treatment that enrich one of the ruptured cells
-
apply_treatment(cells, ruptured_cells, nodes, topology, time)¶ Apply the rupture treatment by enriching one of the cells that is marked as ruptured cells
- Parameters
- cells – array of all cells
- ruptured_cells – boolean array marking the ruptured cells
- nodes – array of all nodes
- topology – topology of the problem
-
initialize_cracked_cell_size(cells, cell_tb_enr)¶ Compute the size of the each part of the newly enriched cell
- Parameters
- cells – cell collection
- cell_tb_enr – id if the cell to be enriched
- Returns
-
property
lump_style¶ Accessor on the mass matrix lumping to be applied
-
property
position_rupture¶ Accessor on the relative position of discontinuity inside the enriched cell
-
Solver¶
Package for solver modules
-
class
solver.NewtonRaphsonBase(function_to_vanish, nb_iterations_max, increment_method)¶ This a base class for 1D non linear Newton-Raphson solver
-
abstract
compute_solution(init_variable)¶ Compute the solution
-
property
function¶ Returns the function to vanish
-
property
nb_iterations_max¶ Returns the maximum iteration number
-
abstract
Utilities¶
Package for utilities modules
-
utilities.timeit_file(filename=None)¶ A decorator allowing to write in the file, the real and cpu execution times of the decorated function
- Parameters
- filename – name of the output file
-
utilities.compute_second_invariant(dev_stress: numpy.array)¶ Compute the square of the second invariant of stress tensor J2 = sqrt(3/2 S:S) where S is the deviatoric part of stress tensor
- Parameters
- dev_stress – deviatoric stress tensor
-
utilities.compute_trace(stress: numpy.array)¶ Compute trace(sigma)
- Parameters
- stress – stress tensor
- Returns
- trace(sigma)
-
utilities.captured_output()¶ A context manager for capturing output (by Jonathon Reinhart)